
SPINAL CORD INJURY
Spinal cord injury stem cell therapy explained
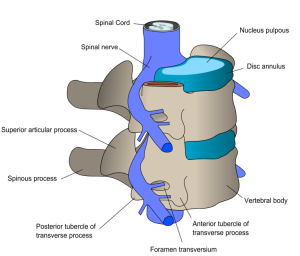 Spinal cord injury is the injury to the spinal cord, a very serious form of trauma with enduring effects on the patient’s daily life. The spinal cord is approximately 18 inches long and extends from brain base at the neck and ending just above the buttocks. It has numerous nerves known as upper motor neurons (UMNs) and is responsible for transmitting signals back and forth from the brain to different parts on the body.
Spinal cord injury is the injury to the spinal cord, a very serious form of trauma with enduring effects on the patient’s daily life. The spinal cord is approximately 18 inches long and extends from brain base at the neck and ending just above the buttocks. It has numerous nerves known as upper motor neurons (UMNs) and is responsible for transmitting signals back and forth from the brain to different parts on the body.
Human beings are in a position to feel pain and move their limbs because messages are sent via the spinal cord, therefore if the spinal cord is damaged some or all of these impulses may not be sent.
What causes spinal cord injuries?
Usually, a spinal cord injury happens as a result of an impulsive accident or event, we list here some of the most common causes of spinal cord injury:
• An aggressive attack like being stabbed or shot
• Diving into very shallow water and hitting the bottom
• Trauma to the face, head, back or the neck region during a motor accident
• Falling from a very high height
• Electrical accident
• Injuries while engaging in sports
• Severe twist of the torso middle portion
Types of spinal cord injuries
All spinal cord injuries are categorized into 2 major categories:
1) Incomplete spinal cord injuries; the spinal cord is partially affected and in this case, the patient retains some functions depending on the degree of the injury. Some of the common types of partial spinal cord include anterior cord syndrome, central cord syndrome and brown-sequard syndrome.
2) Complete spinal cord injuries; this type occurs when the spinal cord is fully damaged and there is no function below the level of injury. However, with proper treatment and physical therapy, it is possible for a patient to regain some functions.
What are the symptoms of spinal cord injury?
• Challenges walking
• Loss of control of bladder or bowels
• Difficulties moving arms and legs
• Headaches
• Unconsciousness
• Pain, pressure, and stiffness in the neck/or back region
• Spreading numbness feelings
• Unnatural head positioning
• Signs of shock
• Loss of libido
• Loss of fertility
• Bedsores
How are spinal cord injuries diagnosed?
Usually, physicians examine patients for spinal cord injuries based on factors like the location, type and the symptoms of the injury. However, no single test can assess 100% these injuries; instead, doctors depend on a number of protocols such as:
• Clinical evaluation; the doctor will keenly observe your symptoms, carry out blood tests, ask detailed questions about your condition and follow your eye movement
• Imaging tests; the doctor may request a magnetic reasoning imaging or radiological imaging to view the spinal column, spinal cord, and brain
Spinal cord injury treatment
Stem cells are found in all multi-cellular organisms and are well known for their remarkable ability to differentiate into almost any other type of cell. Therefore depending on the disease, stem cells can be transplanted into the patient to assist renewal and regeneration of the previously dying cells.
This principle is now being used for a spinal cord injury using stem cells; it assists patients with the recovery process and restores their physiological and sensory ability.
Currently, no stem cell therapy has been approved as a complete cure for spinal injuries. Stem cell therapy is used to improve conditions and symptoms whilst allowing the patient to enjoy a better quality of life after injury.
Two major treatment strategies are being examined by scientists:
Exogenous and endogenous repair.
While in exogenous repair the stem cells are first grown in the lab and then injected into the patient, in endogenous repair stem cells are injected into the injured site and the results depend on the body’s ability to change stem cells into the needed cells.
Current research using adult stem cells
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) have emerged as the leaders due to their proven safety, ability to regulate the immune system’s reaction towards the injury, and to differentiate cell types including neurons and astrocytes.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) have emerged as the leaders due to their proven safety, ability to regulate the immune system’s reaction towards the injury, and to differentiate cell types including neurons and astrocytes.
Other supportive therapies available:
Spinal laser therapy
IV laser therapy
IV Oxygen
Shock Wave Therapy
Peptides injections
Physiotherapy
Enzymes & Nutrition




