
AUTISM
AUTISM STEM CELL THERAPY
What is autism?
Autism spectrum disorder affects an individual’s ability to communicate and form relationships with other people from early childhood. Autism also affects an individual’s ability to use language as well as abstract concepts.
Who is affected by autism?
Autism signs/symptoms start showing from age 2, however, a child can be diagnosed with autism when they are 1.5 years. It is worth noting that some developmental delays linked to autism can be seen even earlier. Parents with concerns that their children are autistic are advised to seek evaluation immediately since early detection increases chances of recovery. Most developmental delays caused by autism can be addressed if they are detected early.
Causes of autism
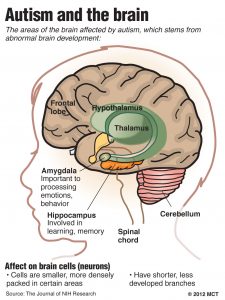 There are still questions on the exact causes of autism; however, there are strong indications that the disease is initiated by a combination of environmental, biologic and genetic influences. Some reasons point to the fact that genes play a crucial role in causing autism. For instance, families with an autistic child have a higher chance (a 5-20% chance) of having another autistic child.
There are still questions on the exact causes of autism; however, there are strong indications that the disease is initiated by a combination of environmental, biologic and genetic influences. Some reasons point to the fact that genes play a crucial role in causing autism. For instance, families with an autistic child have a higher chance (a 5-20% chance) of having another autistic child.
Autism stem cell therapy research have also shown that identical twins have a higher chance of being autistic compared to fraternal twins. Also, children who become autistic usually have parents or close relatives with emotional disorders or mild social impairments, i.e., social/communication problems and repetitive behaviors that are similar to autism. Researchers have also linked autism to an abnormal gene (1 in the 3-5 genes) that interact to cause the disease.
Other factors that have been found to increase autism risks include chemical imbalances, chemicals, viruses or lack of enough oxygen at birth. In some cases, autistic behavior has been linked to; German measles (Rubella) in pregnant mothers, rare genetic disorders like tuberous sclerosis, fragile X syndrome, brain inflammation and untreated phenylketonuria. Autism has also been linked to environmental toxins like pesticides as well as heavy metals (like mercury).
Symptoms of autism
Autism symptoms vary depending on age. Here are some key symptoms; language, social and behavioral signs to look out for in pre-school and school going children.
Language symptoms
Preschool children who are autistic usually have delays speaking i.e. the child may speak very few different words or not speak at all by the time they are age two. Autistic pre-school children also tend to repeat words and phrases more than usual and/or sound very monotonous.
Autistic school going children may exhibit all/most of the above language signs/symptoms as well as others like problems when forming new sentences. They also tend to avoid spoken language, sound very monotonous when they speak and also tend to have problems understanding sarcasm and metaphors.
Social symptoms
In regards to responding to others, autistic children may have problems responding to their name when being called yet they have normal hearing. They may also reject cuddles and react negatively when given tasks.
When interacting with others, autistic pre-school children have problems identifying other children’s/people’s personal space or being tolerant when people invade their personal space. Autistic children also have little interest interacting with their age mates and people in general and will instead prefer playing alone and rarely use facial expressions or gestures when communicating.
Autistic school going children may exhibit all the above signs common among autistic pre-school children and more such as; having problems interacting socially (i.e., greeting people). They may also have problems adapting the tone/content of their speech effectively to different social settings i.e., they may speak formally in a party setting.
Behavioral symptoms
Preschool children with autism tend to exhibit repetitive movements like flicking, rocking and flapping their hands back and forth. They also exhibit a strong dislike or liking for certain foods based on factors like color and texture instead of taste. They may also have unusual sensory interests, i.e., sniffing toys and people inappropriately and may exhibit additional behavioral symptoms like having an unmatched interest in a specific activity or subject.
Autism treatment
There are many ways of treating autism that range from applied behavioral analysis to specialized speech, physical and occupation therapies. All these treatments are focused on dealing with the language, social and behavioral symptoms of autistic patients. Future Clinic revolutionary stem cell therapy program for autism can improve conditions of children suffering with this condition.
Autism stem cell therapy: How stem cell therapy can treat autism
Recent research studies also show that stem cell therapy can be used to treat autism by addressing root causes of the disease like oxygen deprivation, immune function disorder and inflammation. Stem cell therapy for autism utilizes stem cells acquired from the umbilical cord (mesenchymal stem cells). Future Clinic autism stem cell therapy program works toward decreasing increase angiogenesis and blood flow to the brain, immune modulation and inflammation control in patients with autism alleviating autistic symptoms. The therapy has also been found to help in brain development for younger autistic children.
Autism stem cell therapy focuses on restoring lost or impaired neuron connections, forming new neuron connections and speeding up brain reactions by improving synaptic transmission and the development of new neuron connections.
Improvements experienced by autistic patients after stem cell therapy include increased; immunity, metabolism, communication ability, memory and learning capacity. Patients experience improvements in verbal skills, writing skills, self-care skills, attention span, concentration and tolerance to different foods.




