Ataxia Stem Cell Therapy Explained
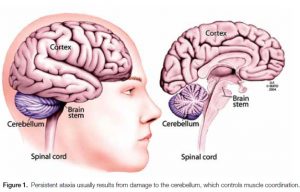
Ataxia is a neurological condition that involves a lack of muscle coordination that affects various involuntary muscle functions like walking, swallowing, eye movement or something as simple as picking something up. Ataxia sufferers have problems with their cerebellum.
The cerebellum is a part of the brain that brings together motion in the human body and when the brain instructs any part of the body to move, electrical signals are conveyed via the spinal cord into peripheral nerves, activating the nerve to contract and start the motion.
Then these signals return through the same peripheral nerves to the cerebellum which inputs vision (the eyes) and balance (from the vestibular system in the inner ear) to facilitate smooth motion. Typically, failure of any of the above signal pathways leads to Ataxia.
There are more than forty different types of this medical condition and as time progresses more findings are expected to be made.
Causes of Ataxia
This condition can either be hereditary and triggered by a genetic defect or acquired after a structural injury to the spinal cord or cerebellum. Genetic Ataxia is either sex linked (the DNA and gene problem is found on the X or Y sex chromosomes) or it is autosomal linked, implying that one of the other twenty-three pairs of chromosomes has the abnormality.
Structural damage may be led by trauma, stroke, multiple sclerosis or any abrasion that reduces the supply of blood into the brain tissues, cerebellum included.
Other potential causes that tend to affect the brain include:
• Poisonings- alcohol is most common poisoning. Mercury poisoning can also lead to Ataxia
• Chemical and electrolyte
• Hormonal abnormalities
• Medication such as lithium
• Recreational drugs such as bhang, ketamine, and phencyclidine (PCP)
• Malnutrition- particularly Vitamin B12 deficiency
• Hypothyroidism
• Immune related disorders where the body is not in a position to digest gluten
There is another category of Ataxia where the underlying cause is not known and this type is named as Idiopathic Ataxia.
Signs and symptoms of Ataxia
Although the signs and symptoms of Ataxia depend on the part of the brain/body affected, the common symptoms revolve around lack of coordination:
• Challenges while walking, maintaining balance which can lead to falling down
• Slurred or slow speech with an abnormal word rhythm
• Difficulty using fingers and hands to perform simple tasks like writing, buttoning a shirt or playing an instrument
• Challenges while swallowing and the victim may choke especially when taking drinks
• Nystagmus (rapid and involuntary eye motions where the eyes move repetitively back and forth)
• Blurred vision and difficulty reading
• Fatigue Can Ataxia be prevented?
Ataxia is an indication of an underlying ailment, therefore it may not be preventable (currently genetic causes are not inevitable). However, evading causes such as toxins and environmental chemicals may reduce the risk of developing this disease.
Ataxia stem cell therapy, diagnosis and treatment duration
 Laboratory tests such as blood, urine, and lumbar puncture among other tests are used to look for electrolytes and toxic chemicals. Computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spinal cord and the brain may also be necessary. Stem cells play a major role in the improvement of Ataxia symptoms and all types of Ataxia have the potential to be treated, but it is important to note that stem cell therapy is not a complete and absolute remedy, Ataxia stem cell therapy improves conditions for the patient.
Laboratory tests such as blood, urine, and lumbar puncture among other tests are used to look for electrolytes and toxic chemicals. Computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spinal cord and the brain may also be necessary. Stem cells play a major role in the improvement of Ataxia symptoms and all types of Ataxia have the potential to be treated, but it is important to note that stem cell therapy is not a complete and absolute remedy, Ataxia stem cell therapy improves conditions for the patient.
The therapy does not change the underlying cause of the cell damage but rather helps provides nutrients to dying brain cells, hence slowing the condition’s progression, it provides relief to the patient’s signs and symptoms and offers improvement in stability and coordination, mental alertness, motor function, speech, swallowing, reduced fatigue and overall health.
Ataxia stem cell therapy: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy from the umbilical cord
Mesenchymal stem cells are responsible for blood cell production in the early stages of intrauterine life; these cells are formed in the fetal phase as cells that later differentiate into cells of various functional systems. Before the umbilical cord sample is harvested, a number of tests including culture, fungal, viral, and immunoglobulin are conducted on the mother’s blood to establish her health condition.
Research has found crucial differences between “Embryonic Stem Cells” and those withdrawn from an adult’s bone marrow; these variations could be attributed to tissue rejections observed when conducting tissue drafting.
Other variations experienced include:
1. Unlike stem cells with umbilical cord origin, stem cells of an adult has immune-related substances
2. Adult stem cells contain Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) which is completely absent in umbilical cord stem cells
3. There is also a variation observed in the type of cytokine presented by stem cells collected from adult tissue and those garnered from the umbilical cord
Despite these differences, stem cells from adult tissue offer fewer opportunities compared to embryonic stem cells. Stem cells obtained from the umbilical cord are abundant probably due to limited mitosis time brought about by longer chromosomal ends.
Ataxia stem cell therapy comprises of 6-8 simple and slightly invasive injections where stem cells are injected into the patient using either a normal “IV Drip System” or through “Intrathecal Injection” conducted after lumbar puncture. These 2 methods increase the procedure’s efficacy besides ensuring the patient’s comfort, convenience, and safety.
Treatment results vary from one patient to another; some patients will have to wait longer but the improvements will be evident eventually. Patients who undergo Ataxia stem cell therapy should observe positive changes in their body a few months after the therapy is performed.





